Private Clouds are enterprise-clouds which are owned by the
organizations and the computing infrastructure is dedicated to the
organizations and the services are not availed to the external users or
other organizations, hence private clouds are also referred as internal
clouds. Private clouds are considered to be more secure than any other
types of deployments of clouds, since the services offered by the
private clouds restricts its usage only to the organization users, and
attacks from external network is filtered at the first step.
Proportionately private clouds are more expensive. Since clouds should
meet the criteria of elasticity, platform infrastructure, hardware
infrastructure must be redundantly available and scalable than required.
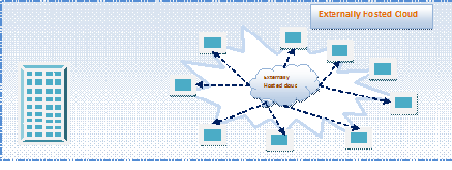
Further private clouds can be of two types: On premise private clouds and externally hosted private clouds. Externally hosted private clouds are not hosted in-house by the organization; instead they are hosted by the third party cloud provider, and are exclusively used by particular organizations in cloud infrastructure. As opposed to expense, externally hosted private clouds are cheaper and little less secure than on premise private clouds.
Pros and Cons
Major issue with development of private clouds consists in vendor lock-in [2]. As most commercial tools were developed independently from one another with a particular focus on solving the respective company’s customers’ problems first, there is little (technical) convergence between the available products. This is also due to the typical development cycle of clouds which typically start as in-house, internal solutions (private clouds) which are then extended to provide (a subset of) capabilities to potential customers (public clouds).
On the other hand the providers will initially want to make use of private clouds and employ for long run will employ so as to address the issues of control versus cost. In combination with the issue of legislation and data distribution, this builds a requirement for industry to have cloud technologies and infrastructures being disposed within required regional or geographical boundaries, so as to ensure that data can remain within a legislative area, if required. This expertise and capability will prove particularly useful to build up new global policies and regulate cloud specific legislations.
Similarly, this knowledge can be employed to provide the environment into new business models and expertise to ensure economic value creation from the employment of cloud systems for various use cases. This information can be used for new systems that automate the cloud configuration even more efficiently. The issue implicitly relates to aspects of Green IT, which currently has found little support in cloud systems, but is a significant issue in current data centre design.
Private Clouds can be thought of to be hosted by an external private cloud provider due to the following reasons

Further private clouds can be of two types: On premise private clouds and externally hosted private clouds. Externally hosted private clouds are not hosted in-house by the organization; instead they are hosted by the third party cloud provider, and are exclusively used by particular organizations in cloud infrastructure. As opposed to expense, externally hosted private clouds are cheaper and little less secure than on premise private clouds.
Pros and Cons
Major issue with development of private clouds consists in vendor lock-in [2]. As most commercial tools were developed independently from one another with a particular focus on solving the respective company’s customers’ problems first, there is little (technical) convergence between the available products. This is also due to the typical development cycle of clouds which typically start as in-house, internal solutions (private clouds) which are then extended to provide (a subset of) capabilities to potential customers (public clouds).
On the other hand the providers will initially want to make use of private clouds and employ for long run will employ so as to address the issues of control versus cost. In combination with the issue of legislation and data distribution, this builds a requirement for industry to have cloud technologies and infrastructures being disposed within required regional or geographical boundaries, so as to ensure that data can remain within a legislative area, if required. This expertise and capability will prove particularly useful to build up new global policies and regulate cloud specific legislations.
Similarly, this knowledge can be employed to provide the environment into new business models and expertise to ensure economic value creation from the employment of cloud systems for various use cases. This information can be used for new systems that automate the cloud configuration even more efficiently. The issue implicitly relates to aspects of Green IT, which currently has found little support in cloud systems, but is a significant issue in current data centre design.
Private Clouds can be thought of to be hosted by an external private cloud provider due to the following reasons
- If demand for service varies with time, i.e. demand is unknown at times.
- Provisioning a data center for the peak load
- To avoid underutilization.
- Support and constant maintenance.
No comments:
Post a Comment